GF-146,Vikram Tower,Sapna Sangeeta Road,Indore(M.P.)
At Karigars -The Jewellery Studio, we believe a jewel represents the most precious moments of a person’s life. So, every piece of Jewellery is made by utmost care and expert craftsmanship. Every piece of jewellery is work of art and should stay in good condition for its lifetime. But over time, the lustre of any jewellery can wear off.
By following some simple tips, your jewellery can be preserved for generations.

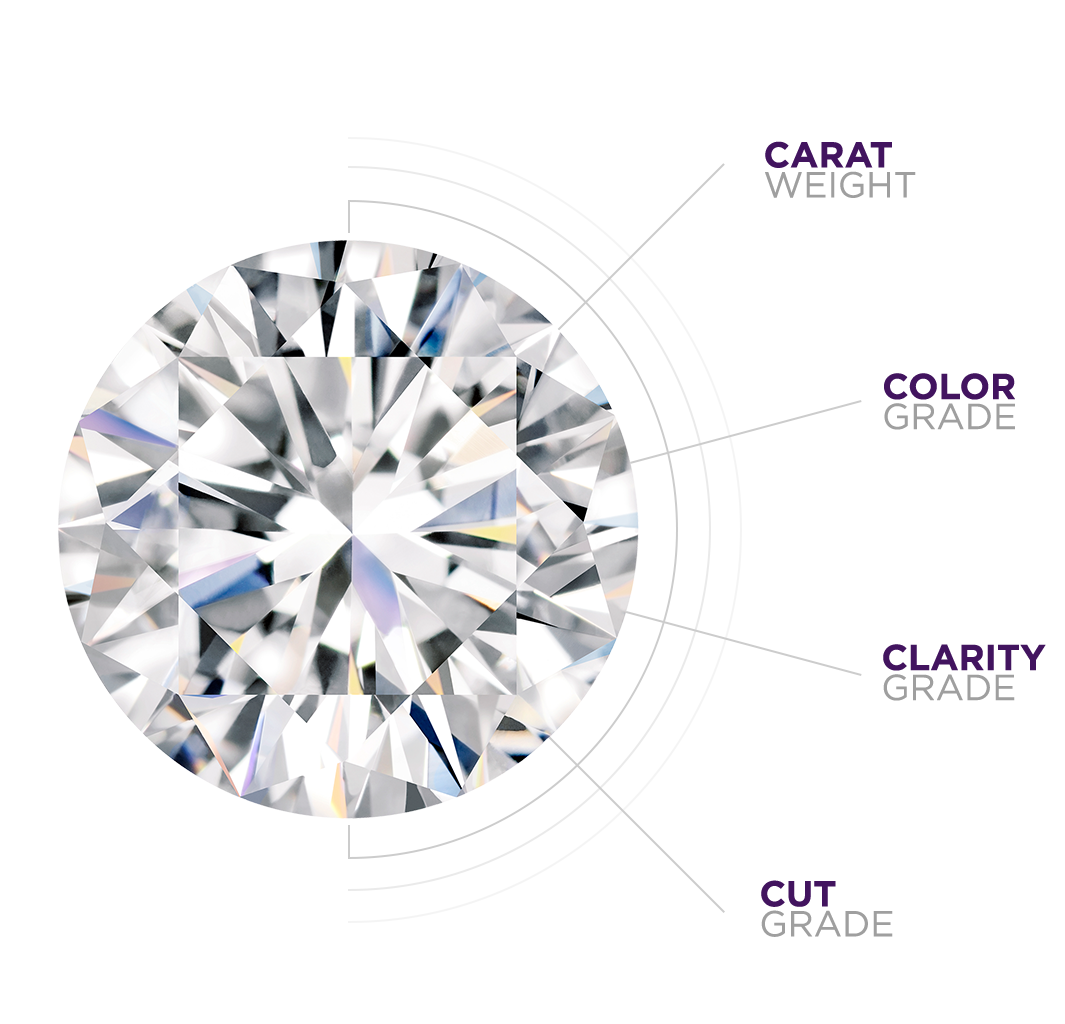
The 4Cs of Diamond Quality is the universal method for assessing the quality of any diamond, anywhere in the world.
Diamond Color means Lack of Color.
The diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value. GIA’s D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value.
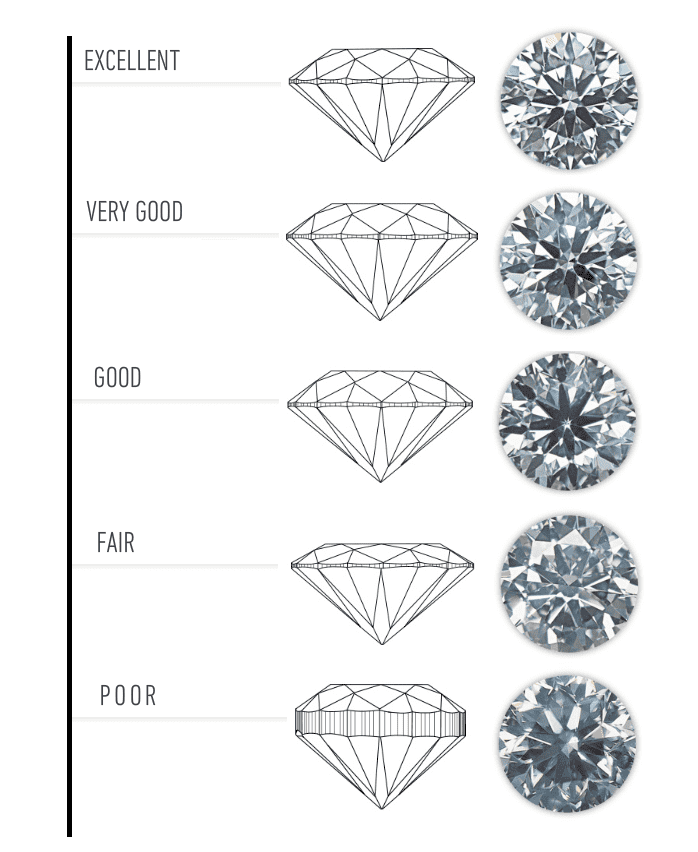
A Diamond’s Cut Unleashes Its Light
To determine the cut grade of the standard round brilliant diamond – the shape that dominates the majority of diamond jewellery – GIA calculates the proportions of those facets that influence the diamond’s face-up appearance. These proportions allow GIA to evaluate how successfully a diamond interacts with light to create desirable visual effects such as:
GIA’s diamond cut grade also takes into account the design and craftsmanship of the diamond, including its weight relative to its diameter, its girdle thickness (which affects its durability), the symmetry of its facet arrangement, and the quality of polish on those facets.
Diamond Clarity Refers to the Absence of Inclusions and Blemishes.
The GIA Diamond Clarity Scale has 6 categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific grades.
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric “carat” is defined as 200 milligrams. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 ‘points.’ This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A jeweller may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its ‘points’ alone. For instance, the jeweller may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a ‘twenty-five pointer.’ Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as ‘one point oh eight carats.’ All else being equal, diamond price increases with diamond carat weight because larger diamonds are rarer and more desirable.